
A strategy inspired by human reasoning processes
This method of prompting is modeled after human metacognition- or "thinking about thinking", an individuals awareness and introspection of their cognitive processes.
The Method
This starts by providing a task or question, including "As you perform this task, follow these steps:" then gives five steps. The example question in the paper is:
The five steps:
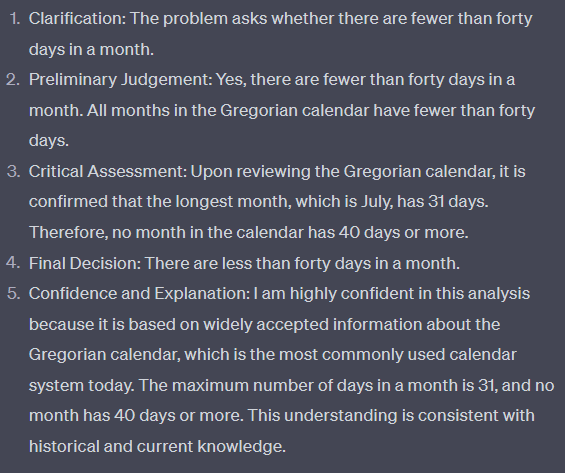
1. Comprehension Clarification - "Clarify your understanding of both questions"
2. Preliminary Judgement - "Make a preliminary identification of similarity based on subject matter, context, and semantic contents."
3. Critical Evaluation - "Critically assess your preliminary analysis. If you are unsure about the initial assessment of the questions being paraphrases, try to reassess it."
4. Decision Confirmation - "Confirm your final decision on whether the questions are paraphrases or not and provide the reasoning for your decision."
5. Confidence Assessment - "Evaluate your confidence in your analysis and provide an explanation for this confidence level."
(The question and steps were fed to the LLM as a single input during experiments with temperature set to zero.)
The general idea is to ensure the model reflects on it’s initial assessment and has a chance to re-evaluate before providing a final answer. Give the LLM a chance to correct it’s initial idea and it’ll often end up with a better idea.
My Tests
Using ChatGPT 3.5 I replicated the examples in the paper as best I could.
Starting with the initial example, I consistently received the opposite conclusion:

 (I regenerated the response 10 times with the same results 100% of the time.)
(I regenerated the response 10 times with the same results 100% of the time.)
I also replicated the examples used for the two common error types (overthinking and overcorrection). In the paper these initially succeeded at stage 2, then failed by stage 4 or 5. My tests instead resulted in consistent successes:
Error Type 1 example: Overthinking


Error Type 2 example: Overcorrection

 My results were opposite to the examples that the researchers provided. Compared to standard prompts ChatGPT succeeded at all three examples.
My results were opposite to the examples that the researchers provided. Compared to standard prompts ChatGPT succeeded at all three examples.
I tested a couple common ChatGPT errors, and with a few regenerations MP managed to get better results over standard prompting.
A classic fail case:
 Improved with MP:
Improved with MP:

Another common mistake:
 Improved with MP:
Improved with MP:
Final notes
The researchers describe the performance of metacognitive prompting as consistently "outstanding", averaging 2%-4.3% better over it's main competitor CoT prompting .
This method can struggle with overthinking and overcorrecting. Basically, if you ask it "are you sure?" it might "fix" it's correct answer and say no. The researchers suggested some potential solutions.
Reference:
Credit to Zea

Fafa
A 6’5 tall man